Underwater noise generated by human activities such as shipping raises concerns about its potential impact on marine life, for instance, by affecting their ability to navigate, communicate, feed, and reproduce. With increased shipping activity along traditional routes and the opening of new shipping lanes, changes in noise intensity and distribution in Canadian waters are expected. Considering that the Canadian Species at Risk Act imposes to protect the habitats of endangered species from degradation, it is imperative to better understand and quantify the impacts of shipping noise on marine life, so that adequate and efficient protective measures can be implemented when necessary.
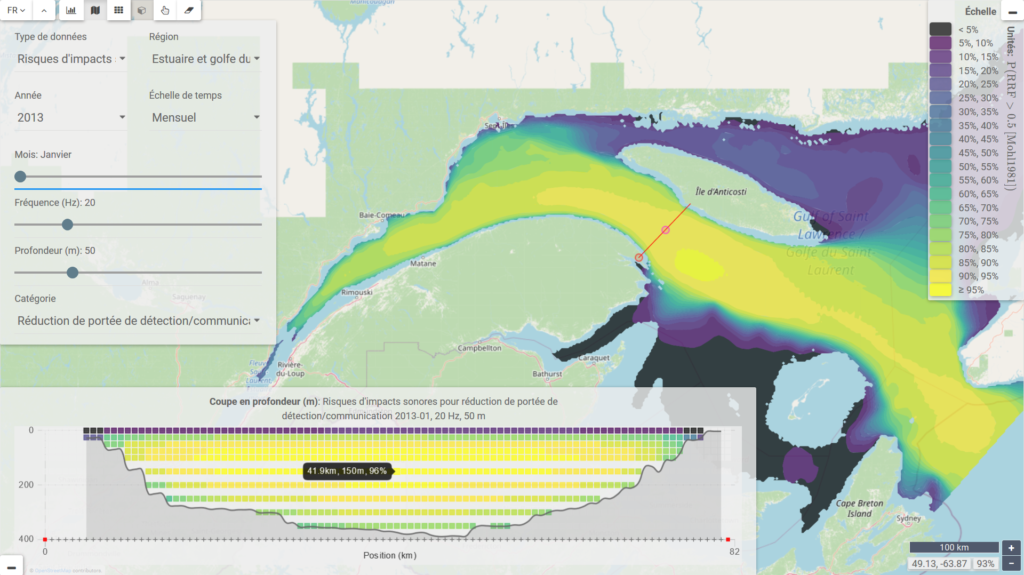
To aid these efforts, the MERIDIAN team based at the Université du Québec à Rimouski and collaborators have developed a web-based, interactive Ocean Soundscape Atlas that will enable users to visualize and explore a wide variety of underwater acoustic maps modeled on many depths, time steps and frequencies. You can view the the Ocean Soundscape Atlas here:
http://soundscape-atlas.uqar.ca/
The Ocean Soundscape Atlas uses validated physical models to determine the levels of noise in Canadian waters due to shipping activity and geophysical environmental noise sources such as wind and waves. In addition, the Atlas contains summarized maps on the risks of having an impact on endangered species such as the North Atlantic right whale. The Atlas will provide a novel interface will facilitate the transfer of scientific information between researchers while contributing to give a better knowledge of the ocean to the public. The Atlas will allow managers and policy makers to monitor trends in the state of the ocean acoustic environment, and hence ensure more timely, effective, and efficient marine environmental conservation and management of the valued and especially protected marine species.
As part of this project, we are also developing a new software library to facilitate the modelling of ocean ambient noise due to environmental agents such as waves and rain. Named Kadlu, the library can be found at https://docs.meridian.cs.dal.ca/kadlu/.